Solving common problems with indoor pool heating systems is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and enjoyable swimming experience. From chilly water to unexpectedly high energy bills, issues with your pool’s heating system can quickly dampen the fun. This guide delves into the most frequent problems, providing practical troubleshooting steps, preventative maintenance strategies, and insights into energy-efficient solutions. We’ll cover everything from identifying the source of a malfunctioning heater to understanding the long-term benefits of regular professional service, empowering you to keep your indoor pool warm and inviting year-round.
Common Indoor Pool Heating System Problems
Maintaining a consistently warm indoor pool requires a reliable heating system. However, several common issues can disrupt the ideal temperature and lead to increased energy costs or even system failure. Understanding these problems and their causes is crucial for proactive maintenance and preventing costly repairs.
Insufficient Heating
Insufficient heating, where the pool water fails to reach or maintain the desired temperature, is a frequent complaint. This problem often stems from several interconnected factors. A malfunctioning heating element, whether it’s a gas heater, heat pump, or boiler, is a primary culprit. Scale buildup within the heat exchanger can significantly reduce its efficiency, hindering heat transfer to the water.
Inadequate circulation of water through the heating system prevents even heat distribution, leading to cold spots in the pool. Finally, air leaks in the pool’s plumbing system can also contribute to heat loss. Neglecting these issues can lead to uncomfortable swimming temperatures, increased energy consumption as the system struggles to compensate, and ultimately, premature wear and tear on the equipment.
Troubleshooting indoor pool heating often involves identifying leaks or inefficient pumps. A major overhaul might be necessary, especially if you’re dealing with an older system; check out this guide on cost effective ways to renovate an old swimming pool to see if a full renovation makes more sense than piecemeal repairs. Ultimately, the best solution for your heating problems depends on the age and condition of your entire pool system.
Uneven Water Temperature
Another common problem is uneven water temperature distribution within the pool. This often results from poor circulation. The pool’s pump and filter system play a crucial role in ensuring that heated water is properly mixed throughout the entire pool volume. A weak pump, clogged filter, or improperly sized plumbing can lead to areas of significantly different temperatures. In addition, poorly designed or maintained ductwork in a system using forced-air heating can also cause uneven distribution.
Consequences of ignoring uneven temperatures include discomfort for swimmers, potentially creating areas too cold or too hot for safe and enjoyable swimming. It can also contribute to the development of stagnant water areas, promoting bacterial growth.
High Energy Consumption
Unexpectedly high energy bills directly related to pool heating can indicate underlying problems. This often points to inefficient operation of the heating system. Factors like scale buildup, as previously mentioned, significantly reduce the heating efficiency. Similarly, air leaks in the pool’s plumbing or building envelope can cause significant heat loss, forcing the system to work harder to maintain the set temperature.
A poorly insulated pool enclosure also exacerbates the problem. Neglecting these issues results in unnecessarily high energy costs, contributing to a significant financial burden over time. For example, a system with a 10% heat loss due to leaks could easily increase energy bills by 10% or more.
System Malfunctions
Complete system failure or frequent breakdowns can disrupt pool use entirely. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty components like the heating element itself, a failing control system (thermostat or other sensors), or issues with the pump or circulation system. Electrical problems, such as short circuits or blown fuses, can also shut down the entire system.
Ignoring minor malfunctions or postponing necessary repairs can lead to catastrophic failure, requiring extensive and costly repairs or even complete system replacement. This downtime can lead to significant inconvenience and financial losses, particularly for commercial pools.
Leaks in the Pool or Plumbing, Solving common problems with indoor pool heating systems
Leaks in the pool structure or its associated plumbing represent a significant problem. Leaks lead to water loss, requiring more frequent refilling, increasing water and chemical costs. They also necessitate constant heating of replacement water, further driving up energy consumption. Moreover, persistent leaks can lead to structural damage over time, particularly in the case of significant water loss.
Ignoring leaks can cause significant financial and structural problems, leading to far greater costs to repair in the long run than addressing the issue promptly.
Troubleshooting Techniques for Heating System Issues
Troubleshooting a malfunctioning indoor pool heating system can seem daunting, but a systematic approach can quickly pinpoint the problem. By carefully checking key components and understanding their interdependencies, you can often resolve issues without needing a professional. This section details common troubleshooting steps for various heating system elements.
Malfunctioning Heater Troubleshooting
A malfunctioning heater is often indicated by a lack of heat or unusual noises. Before attempting any repairs, always turn off the power to the heater to prevent electrical shock. Basic checks include verifying power supply to the unit, inspecting the gas line (if applicable) for leaks, and examining the heater’s circuit breaker or fuse for tripping. Look for any visible signs of damage, such as loose wiring or corrosion.
If the heater has a digital display, error codes may provide valuable clues. Consulting the heater’s manual for troubleshooting guides and error code explanations is crucial. If the problem persists after these checks, professional assistance is recommended.
Pool Pump and Filter Efficiency Check
The pool pump and filter are vital for efficient heat distribution. A clogged filter restricts water flow, reducing the heater’s effectiveness and potentially causing overheating. A step-by-step guide follows:
- Inspect the filter pressure gauge: A significantly higher-than-normal pressure reading indicates a clogged filter. The ideal pressure difference between the gauge reading and the clean filter reading should be within the manufacturer’s specifications, usually a few PSI.
- Backwash the filter: If the pressure is high, backwash the filter according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This process cleans the filter media by reversing the water flow.
- Check for leaks: Inspect all connections and seals on the pump and filter for leaks. Leaks reduce water flow and can damage the equipment.
- Examine the pump impeller: Access the pump impeller and check for any damage or debris. A damaged impeller reduces pump efficiency. Replace it if necessary.
- Check pump motor operation: Listen for unusual noises like grinding or humming, which may indicate motor issues.
If the problem persists after these steps, the pump or filter may require professional repair or replacement.
Heating System Thermostat Issues
The thermostat controls the heating system’s operation. Problems with the thermostat can lead to inconsistent heating or complete system failure. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Check thermostat power: Ensure the thermostat is receiving power. This often involves checking the circuit breaker or fuse.
- Inspect thermostat wiring: Loose or damaged wiring can disrupt the thermostat’s connection to the heater. Carefully examine all wiring connections.
- Test the thermostat’s functionality: Try adjusting the thermostat’s settings to see if the heater responds. If there’s no response, the thermostat may need replacement.
- Clean the thermostat: Dust or debris can interfere with the thermostat’s operation. Gently clean the thermostat with a soft brush or compressed air.
Replacing a faulty thermostat is often a straightforward DIY repair, but always ensure the power is off before handling electrical components.
Low Water Temperature Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart visually simplifies troubleshooting low water temperature. Imagine a flowchart starting with “Low Water Temperature Detected?”. If yes, proceed to “Check Heater Operation”. If the heater isn’t functioning, follow the “Malfunctioning Heater Troubleshooting” steps Artikeld above. If the heater is working, proceed to “Check Pool Pump and Filter Efficiency”, following the steps detailed earlier.
If issues persist after checking the pump and filter, the next step would be “Check Thermostat Functionality,” following the steps Artikeld in the “Heating System Thermostat Issues” section. If problems remain after all these steps, the flowchart concludes with “Consult a Pool Professional”. Each step within the flowchart should branch out to the next appropriate check based on the results of the previous step.
This systematic approach ensures thorough troubleshooting.
Maintenance and Prevention Strategies
Proactive maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of your indoor pool heating system and preventing costly repairs. Regular upkeep minimizes downtime, ensures consistent heating, and ultimately saves you money in the long run. A well-maintained system also contributes to a safer and more enjoyable swimming experience.Regular maintenance encompasses several key areas, including scheduled inspections, filter cleaning, chemical balancing, and addressing any minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
By implementing a preventative maintenance plan, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and ensure your pool heating system operates efficiently and effectively for years to come.
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
A comprehensive preventative maintenance schedule should be tailored to your specific heating system and pool usage. However, a general guideline includes tasks performed on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. Adherence to this schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.
| System Type | Maintenance Task | Frequency | Cost (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Pump | Clean condenser coils and filters | Monthly | $20 – $50 (DIY); $50 – $150 (Professional) |
| Gas Heater | Inspect burner and flame sensor | Quarterly | $0 (DIY); $75 – $150 (Professional) |
| Electric Heater | Check electrical connections and wiring | Annually | $0 (DIY, with basic electrical knowledge); $100 – $200 (Professional) |
| All Systems | Check water level and chemical balance | Weekly | $0 (DIY) |
| All Systems | Annual Professional Inspection and Servicing | Annually | $200 – $500 |
Importance of Regular Filter Cleaning and Chemical Balancing
Regular filter cleaning is crucial for maintaining water clarity and preventing the buildup of debris that can damage your heating system. A clogged filter restricts water flow, reducing heating efficiency and potentially causing overheating. Similarly, maintaining proper chemical balance prevents corrosion and scaling within the heating system components, prolonging their lifespan. Ignoring these aspects can lead to premature wear and tear, requiring costly repairs or replacements.
For example, neglecting filter cleaning can lead to a 20% reduction in heating efficiency, increasing energy costs significantly.
Dealing with high energy bills from your indoor pool heater? One way to significantly reduce those costs is by minimizing heat loss. A great solution is to build a DIY pool cover to retain heat, and you can find helpful instructions on how to do just that by checking out this guide on building a DIY swimming pool cover for winter protection.
This simple project can drastically improve the efficiency of your heating system, saving you money in the long run and making your indoor pool more cost-effective to operate.
Benefits of Annual Professional Inspections and Servicing
Annual professional inspections and servicing offer several key benefits. A qualified technician can identify potential problems before they become major issues, saving you money on repairs. They can also perform essential maintenance tasks, such as cleaning internal components, checking for leaks, and ensuring proper operation. Professional servicing also helps to optimize your system’s efficiency, reducing energy consumption and lowering your utility bills.
Furthermore, many manufacturers require annual servicing to maintain warranties. For example, a timely professional inspection might uncover a small leak in a heat exchanger, preventing a much more expensive repair later.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Keeping your indoor pool heated efficiently is crucial, both for comfort and to minimize operational costs. This section explores various strategies to significantly reduce energy consumption associated with pool heating. We’ll examine different heating systems, the impact of insulation, and methods for optimizing your existing setup.
Choosing the right heating system is paramount for energy efficiency. Different systems offer varying levels of efficiency and are suited to different pool sizes and budgets. Proper insulation minimizes heat loss, and optimizing the system involves careful consideration of factors like temperature settings, filtration cycles, and even the pool’s cover.
Comparison of Energy-Efficient Pool Heating Systems
Several heating systems offer varying degrees of energy efficiency. Heat pumps are generally considered the most efficient option for indoor pools, as they transfer heat from the surrounding air rather than generating it directly, like gas heaters. Solar heating systems utilize renewable energy, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution, although their effectiveness depends heavily on sunlight availability. Gas heaters, while offering rapid heating, tend to be less energy-efficient than heat pumps in the long run.
The choice depends on factors such as climate, budget, and environmental concerns. A professional assessment can help determine the best option for your specific needs.
The Role of Proper Insulation in Reducing Energy Consumption
Effective insulation significantly reduces heat loss from the pool and its surrounding environment. This includes insulating the pool itself (using specialized pool insulation blankets), the walls and ceiling of the pool room, and even the pipes carrying the heated water. Proper insulation minimizes the workload on the heating system, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
For example, a poorly insulated pool room might lose 20% more heat than a well-insulated one, translating to a substantial increase in energy bills. Investing in high-quality insulation materials can provide a significant return on investment over time.
Strategies for Optimizing Pool Heating System Efficiency
Optimizing your pool’s heating system involves several key strategies. Maintaining the correct water temperature is crucial. Overheating the pool wastes energy. Regularly cleaning and maintaining the pool’s filter system ensures efficient water circulation and heat distribution. Using a pool cover when the pool is not in use dramatically reduces evaporative heat loss.
Regularly scheduling maintenance checks can identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reducing energy waste caused by malfunctioning equipment. Finally, implementing smart controls, such as timers and programmable thermostats, allows for precise control over the heating system, further optimizing energy consumption.
Calculating Energy Savings
Calculating energy savings involves comparing energy consumption before and after implementing energy-efficiency improvements. This can be done by monitoring energy usage through your utility bills. For example, if your monthly energy bill for pool heating was $500 before improvements and dropped to $350 after implementing insulation and optimizing the heating system, the savings would be $150 per month, or $1800 annually.
More sophisticated methods involve using energy audit software or consulting with energy efficiency professionals who can conduct a thorough assessment and provide detailed calculations based on your specific circumstances. These assessments often take into account factors such as the pool’s size, the type of heating system, and the climate. For instance, a heat pump system might offer a 30-50% reduction in energy consumption compared to a traditional gas heater, resulting in substantial savings over the lifespan of the equipment.
Precise savings will depend on individual circumstances.
Repair and Replacement Options
Repairing or replacing your indoor pool heater is a significant decision, impacting both your budget and the longevity of your pool’s heating system. Understanding the different types of heaters and their associated costs is crucial for making an informed choice. This section will Artikel the various options available, helping you weigh the pros and cons of repair versus replacement.Different Types of Pool Heaters and Their Repair Requirements
Pool Heater Types and Repair Needs
Indoor pool heating systems commonly utilize gas heaters, heat pumps, or electric heaters. Gas heaters, often employing natural gas or propane, typically require repairs related to igniters, burners, heat exchangers, or gas control valves. These repairs can range from simple part replacements to more complex servicing requiring specialized tools and expertise. Heat pumps, which transfer heat from the surrounding air to the pool water, may need repairs to their compressors, fans, or refrigerant circuits.
Electric heaters, while generally simpler in design, can experience issues with heating elements, thermostats, or electrical connections. The complexity and cost of repairs vary greatly depending on the specific heater type and the nature of the malfunction.
Factors Influencing Replacement Decisions
Several factors should be considered when deciding whether to repair or replace a faulty pool heater. The age of the heater is a primary consideration; older units may be more prone to repeated breakdowns, making replacement a more cost-effective long-term solution. The severity and cost of the required repairs compared to the overall cost of a new unit is another critical factor.
Energy efficiency is also important; newer heaters often boast significantly improved energy efficiency ratings, leading to lower operating costs over the unit’s lifespan. Finally, the availability of parts for older models can influence the decision; if parts are scarce or expensive, replacement might be the more practical choice.
Repair versus Replacement Cost Comparison
A direct cost comparison between repair and replacement is difficult to provide without specific details about the heater, the nature of the malfunction, and labor costs in your area. However, a general guideline is that repairs for minor issues, such as replacing a faulty thermostat or igniter, might cost a few hundred dollars. More substantial repairs, involving components like heat exchangers or compressors, can easily reach several thousand dollars.
Replacing an entire pool heater typically ranges from a few thousand dollars for a basic unit to tens of thousands for high-end models with advanced features. Therefore, a thorough cost analysis, including repair estimates and new heater quotes, is essential before making a decision.
Repair Scenarios and Associated Costs
Let’s consider some examples of repair scenarios and their associated costs:
- Scenario 1: Faulty Thermostat. Replacing a faulty thermostat in a gas heater is typically a relatively inexpensive repair, costing around $100-$300, including parts and labor.
- Scenario 2: Leaky Heat Exchanger. Repairing or replacing a leaky heat exchanger in a gas heater is a more complex and expensive repair, potentially costing $1000-$3000 or more depending on the heater model and labor rates.
- Scenario 3: Malfunctioning Compressor in a Heat Pump. Repairing or replacing a compressor in a heat pump is a major repair that could easily cost $2000-$5000 or more, due to the specialized equipment and expertise required.
These examples highlight the significant cost differences between minor and major repairs. It’s crucial to obtain multiple quotes from reputable pool service technicians before committing to any repair or replacement.
Improving Water Quality and Hygiene
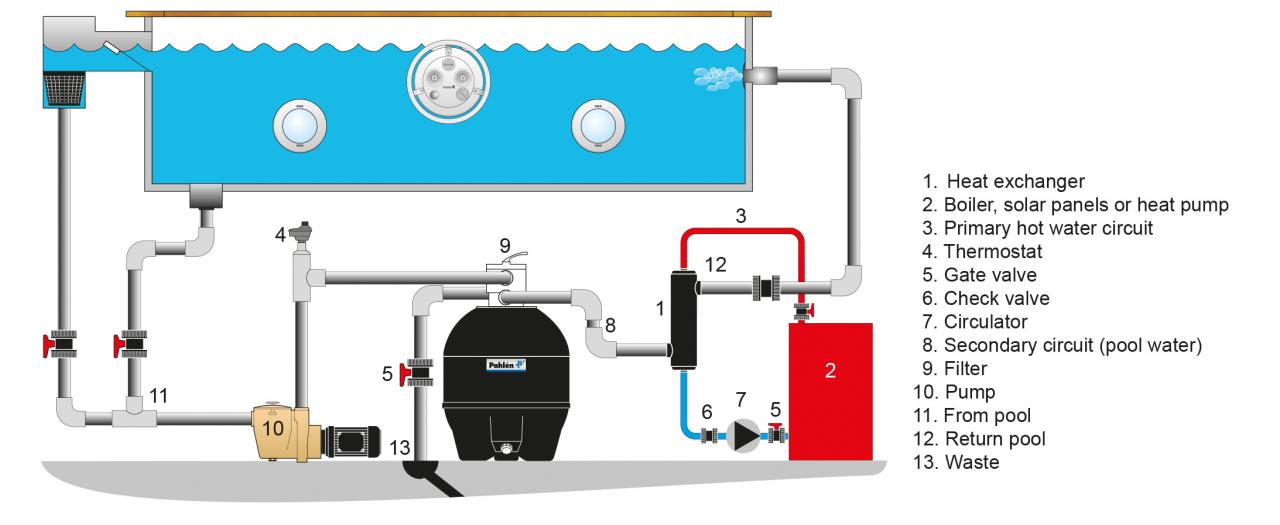
Source: pahlen.com
Maintaining optimal water quality in an indoor pool is crucial for both hygiene and the longevity of the pool’s equipment. Water temperature plays a significant role in this process, influencing not only swimmer comfort but also the growth of harmful bacteria and the effectiveness of sanitizing chemicals.Proper heating contributes significantly to maintaining sanitary conditions within the pool environment. Warmer water, within a safe and comfortable range, promotes the effectiveness of disinfectants like chlorine, reducing the risk of bacterial and algal growth.
Conversely, colder water can hinder the disinfecting process and potentially lead to a breeding ground for pathogens.
Water Temperature and Bacterial Growth
The relationship between water temperature and bacterial growth is directly proportional within a specific range. A graph depicting this relationship would show a curve rising steadily as temperature increases from cool to ideal pool temperatures. This upward trend indicates accelerated bacterial reproduction. The curve would then plateau or slightly decrease at extremely high temperatures due to the lethal effects of heat on most bacteria.
However, temperatures too far outside the ideal pool range should be avoided. The graph’s x-axis would represent water temperature (in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit), and the y-axis would represent bacterial colony-forming units (CFUs) per milliliter of water. The visual would clearly show an optimal temperature range where bacterial growth is minimized while still maintaining comfortable swimming conditions.
A shaded area would highlight the ideal range for minimizing bacterial growth and maximizing disinfectant effectiveness.
Filtration and Chemical Balance
Effective filtration and chemical balance are inseparable from the benefits of proper heating in maintaining pool hygiene. Heating alone is insufficient; a well-maintained filtration system removes debris and organic matter that would otherwise provide nutrients for bacterial growth. Simultaneously, a balanced chemical environment, achieved through regular testing and adjustment of chlorine, pH, and alkalinity levels, ensures that the water remains disinfected and safe for swimmers.
The interplay between these three factors – heating, filtration, and chemical balance – creates a synergistic effect, maximizing water quality and minimizing the risk of health hazards.
Final Wrap-Up: Solving Common Problems With Indoor Pool Heating Systems
Maintaining your indoor pool’s heating system effectively involves a blend of proactive maintenance, prompt troubleshooting, and informed decision-making regarding repairs or replacements. By understanding the common issues, implementing preventative measures, and leveraging energy-efficient solutions, you can ensure your pool remains a source of comfort and enjoyment for years to come. Remember, regular checks, timely maintenance, and professional assistance when needed will significantly contribute to the longevity and efficiency of your system, keeping your swimming experience consistently pleasant and cost-effective.
Key Questions Answered
What should I do if my pool heater isn’t turning on?
First, check the circuit breaker to ensure power is supplied to the heater. Then, verify that the heater’s gas supply (if applicable) is on and that there are no leaks. If the problem persists, contact a qualified technician.
How often should I clean my pool filter?
The frequency depends on your pool’s usage and type of filter. Backwashing a sand filter might be needed weekly during heavy use, while cartridge filters often require cleaning every 2-4 weeks. Consult your filter’s manual for specific recommendations.
What are the signs of a failing pool heater?
Signs include inconsistent heating, unusual noises, leaking, and a noticeable decrease in water temperature despite the heater being on. A pilot light that won’t stay lit (for gas heaters) is also a major warning sign.
How can I reduce my pool heating costs?
Consider using a pool cover to reduce heat loss, optimizing your pool’s filtration system, investing in an energy-efficient heater, and ensuring proper insulation around the pool.
What’s the best way to maintain water quality in a heated pool?
Maintain proper chemical balance (chlorine, pH, alkalinity), regularly clean the filter, and ensure proper circulation. Warmer water can lead to faster algae growth, so regular testing and adjustments are vital.










