Smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling solutions are revolutionizing how we handle kitchen waste. Imagine a future where sorting recyclables is effortless, and disposal is automated and efficient. This isn’t science fiction; innovative systems are already emerging, combining smart technology with sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact and maximize convenience. We’ll explore the different types of systems available, from automated marvels to more manual options, and delve into the integration with other smart home devices.
Discover how sensor technology, AI, and intuitive designs are transforming waste management in the kitchen, making it simpler, greener, and more efficient than ever before.
Types of Smart Kitchen Waste Disposal Systems
Smart kitchen waste disposal systems are revolutionizing how we handle food scraps and other kitchen waste, offering convenience, hygiene, and environmental benefits. These systems range from simple, automated units to more sophisticated models with integrated recycling capabilities. Understanding the different types available helps consumers choose the best option for their needs and lifestyle.
Smart Waste Disposal System Types
Several types of smart kitchen waste disposal systems cater to varying needs and budgets. They differ primarily in their mechanisms for waste processing and their level of automation. Some systems focus solely on disposal, while others incorporate recycling features.
| System Type | Mechanism | Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated In-Sink Disposers | Grinds food waste into small particles using a powerful motor and then flushes them down the drain. Some models feature sound dampening technology. | Automatic operation, often with various speed settings; some include odor control systems; usually requires plumbing connection. | $200 – $800 |
| Smart Compost Bins | Utilizes a combination of aeration and controlled temperature to accelerate the composting process. Some models include sensors to monitor moisture and temperature, alerting users when the bin needs attention. | Automated process, reduces odors; requires emptying less frequently than traditional compost bins; some offer mobile app integration for monitoring. | $150 – $500 |
| Under-Counter Waste Disposal Systems | These systems typically grind food waste and either flush it down the drain or collect it in a sealed container for later disposal or composting. Some models incorporate filtration systems to prevent clogging. | Often quieter than in-sink disposers; can be more discreet; some models offer separate compartments for different types of waste. | $300 – $1000+ |
| Integrated Recycling and Disposal Systems | These advanced systems often combine features of multiple disposal methods, allowing users to sort waste into different compartments for recycling, composting, and disposal. They may include sensors for automatic sorting and/or compacting. | Highly efficient waste management; reduces landfill waste; often includes smart features like app integration and waste level monitoring; generally more expensive. | $500 – $2000+ |
Automated vs. Manual Systems, Smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling solutions
The choice between automated and manual systems depends largely on individual preferences and priorities. Automated systems offer convenience and efficiency, reducing the effort involved in waste disposal. However, they typically come with a higher price tag and may require more maintenance. Manual systems, on the other hand, are generally more affordable but demand more active participation from the user.
Smart Recycling Solutions for the Kitchen
Smart recycling bins are revolutionizing how we handle kitchen waste, making the process more efficient and environmentally friendly. These systems go beyond simple sorting, employing advanced technologies to streamline waste management and reduce landfill contributions. They offer a convenient and effective way to participate in responsible waste disposal.Smart recycling solutions leverage a combination of sensor technology and AI algorithms to automate and optimize the sorting process.
This intelligent approach significantly improves the accuracy of waste separation, minimizing contamination and maximizing recycling rates. The benefits extend to both individual households and larger waste management systems, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Features of Smart Recycling Bins
Smart recycling bins typically include several key features designed to simplify and enhance the waste sorting process. These features often work together to provide a seamless user experience and ensure accurate waste separation. Many models offer multiple compartments for different recycling streams (plastics, paper, glass, etc.), each with its own sensor to monitor fill levels. Some also include automated compaction mechanisms to maximize capacity.
Other features may include weight sensors to provide feedback on the amount of waste being disposed of, and connectivity features to provide real-time data on bin fill levels and recycling performance. This information can be used to optimize collection schedules and improve overall waste management efficiency.
Sensor Technology and AI Algorithms in Smart Recycling
Sensor technology plays a crucial role in the functionality of smart recycling bins. Infrared, ultrasonic, and weight sensors are commonly used to detect the type and quantity of waste being deposited. These sensors provide data to the AI algorithms that power the system’s decision-making process. The AI algorithms analyze the sensor data, comparing it to a database of known materials and characteristics to identify the type of waste.
This allows the system to automatically direct the waste to the appropriate compartment, ensuring accurate sorting. Furthermore, these algorithms can learn and adapt over time, improving their accuracy and efficiency as they process more data. For example, a system might learn to differentiate between different types of plastics based on their weight and shape.
Waste Sorting Process in a Smart Recycling System
The following description illustrates the process: A user places waste into the smart recycling bin’s opening. Sensors within the bin detect the item’s characteristics (shape, size, weight, material type – determined through spectral analysis if implemented). The data is transmitted to the onboard processing unit or a cloud-based AI system. The AI algorithms analyze the data and classify the waste. Based on the classification, the system directs the waste to the appropriate compartment (e.g., plastics, paper, glass, organic). The bin’s internal mechanisms (robotic arms or gravity-fed chutes) move the waste into the correct compartment. Fill level sensors monitor the compartments, signaling when they are full and requiring emptying. Data on the types and amounts of waste sorted is recorded and can be accessed via an app or web portal, providing insights into recycling habits.
Integration with Smart Home Ecosystems: Smart Kitchen Waste Disposal And Recycling Solutions
Smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling systems are increasingly designed for seamless integration with other smart home devices, enhancing convenience and efficiency in waste management. This integration leverages existing home automation infrastructure and expands the functionality of both the waste management system and the broader smart home network.The benefits of connecting these systems to your broader smart home network are significant.
Integration with various platforms allows for centralized control, automated processes, and data-driven insights into waste generation and recycling habits. This ultimately leads to more sustainable practices and a more streamlined household routine.
Voice Assistant Integration
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant offer a hands-free way to interact with smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling systems. Imagine effortlessly commanding your system to open, close, or initiate a cleaning cycle simply by voice command. This is particularly beneficial when your hands are full or when you’re multitasking in the kitchen. Furthermore, voice integration can provide real-time status updates on the system’s operation, such as filling levels or maintenance alerts.
For example, a user could ask their smart speaker, “Alexa, how full is the compost bin?”, and receive an immediate response. This level of accessibility improves the user experience and encourages consistent engagement with the waste management system.
Home Automation Platform Integration
Many smart kitchen waste systems are compatible with popular home automation platforms like Apple HomeKit, Samsung SmartThings, and IFTTT (If This Then That). This integration allows for sophisticated automation scenarios. For instance, a user could set up a rule where the waste disposal system automatically activates after the dishwasher completes its cycle, collecting food scraps efficiently. Another scenario could involve integrating with smart sensors in the kitchen; a smart bin could automatically send a notification to your smartphone when it’s nearly full, prompting you to empty it before it overflows.
These automated actions not only save time and effort but also help to prevent unpleasant odors and potential hygiene issues.
Improved Convenience and Efficiency Examples
Consider a scenario where a user is preparing a meal. Using voice commands, they instruct their smart waste disposal system to activate, disposing of food scraps directly as they cook. After the meal, the system automatically sends a notification to the user’s smartphone, indicating the need for emptying. This eliminates the need for manual intervention, reduces odors, and simplifies the cleaning process.
Another example involves smart recycling systems that use image recognition to automatically sort waste into the correct compartments. This reduces manual sorting and minimizes contamination, leading to higher recycling rates and a more efficient waste management process. These examples illustrate how integration improves not only convenience but also the overall efficiency of kitchen waste management.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling systems offer significant environmental benefits, contributing to a more sustainable future by minimizing waste and maximizing resource recovery. These systems move us away from traditional landfill-dependent waste management towards a more circular and environmentally responsible approach. Their impact extends beyond individual households, contributing to broader community and global sustainability efforts.The primary environmental benefit stems from a drastic reduction in landfill waste.
Landfills are significant sources of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, a potent climate change contributor. By diverting organic waste and recyclables from landfills through efficient sorting and processing, these systems drastically decrease the volume of waste sent to landfills, thus reducing methane emissions and lessening their environmental footprint. Furthermore, the recovery of recyclable materials conserves natural resources and reduces the need for virgin materials, lowering the overall environmental impact of manufacturing processes.
Reduced Landfill Waste and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Smart waste disposal systems actively decrease the amount of organic waste ending up in landfills. This is achieved through efficient separation and processing, often involving composting or anaerobic digestion. These processes break down organic matter, producing biogas (a renewable energy source) and compost (a valuable soil amendment), significantly reducing the volume of material destined for landfills. For example, a household using a smart system might divert 50% of its kitchen waste from landfills, a substantial reduction in the overall waste stream.
This translates to less methane production, a critical factor in mitigating climate change. Anaerobic digestion of food waste, in particular, can produce biogas that can be used to generate electricity, further reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Contributions
Smart systems actively promote resource recovery by efficiently separating recyclables from other waste streams. This allows for higher-quality recycling, leading to better resource utilization. Consider a smart system accurately sorting glass, plastic, and metal, increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling programs. This process reduces the demand for new raw materials, conserving natural resources and minimizing the environmental impact associated with extraction and processing.
- Reduced reliance on virgin materials: Recycled materials from smart systems reduce the need for extracting new resources, conserving natural resources and minimizing habitat destruction.
- Decreased energy consumption: Manufacturing products from recycled materials generally requires less energy than using virgin materials, reducing carbon emissions.
- Lower water consumption: Recycling processes often use less water than producing new materials, conserving this vital resource.
- Reduced pollution: The extraction and processing of virgin materials often leads to air and water pollution. Recycling significantly reduces these pollutants.
- Promotion of compost production: Organic waste processed through smart systems creates compost, a valuable soil amendment that reduces the need for chemical fertilizers.
User Experience and Design Considerations
A truly successful smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling system hinges on a user-friendly experience. Ease of use and intuitive design are paramount to encourage adoption and ensure consistent, effective waste management. Poor design can lead to frustration, misuse, and ultimately, a failure to achieve the system’s environmental goals.The importance of intuitive interfaces and clear instructions cannot be overstated.
Users should be able to understand and operate the system with minimal effort, regardless of their technical proficiency. Complicated instructions or confusing interfaces will lead to user abandonment and negate the benefits of a smart system. The design should prioritize simplicity and clarity, guiding users through the process effortlessly.
Intuitive Interface Design
An ideal user interface should prioritize visual clarity and ease of navigation. Imagine a touchscreen interface with large, clearly labeled icons representing different waste categories (e.g., compost, recycling, landfill). Each icon could be accompanied by a simple image representing the type of waste it accepts. For example, the compost icon might show a picture of fruit peels, while the recycling icon might display a familiar recycling symbol.
The screen could also display the current fill levels of each compartment, using a simple bar graph or percentage indicator. This visual representation allows users to quickly assess the status of their waste bins and take action when necessary. Furthermore, the system could provide haptic feedback (gentle vibrations) to confirm successful waste disposal, adding another layer of intuitive interaction.
Error messages should be presented in plain language, avoiding technical jargon. For instance, instead of “Sensor Malfunction Error Code 12,” the system might display “Please check the sensor; it may be obstructed.” This ensures that users understand the problem and can take appropriate steps to resolve it.
Voice Control Integration
Voice control offers a convenient and hands-free way to interact with smart kitchen waste disposal systems. Imagine a system that responds to simple voice commands like, “Add to compost,” or “Dispose of plastic bottle.” This feature is particularly useful when users have their hands full or are busy preparing food. The system could also provide voice feedback confirming the action or indicating if the waste type is not recognized.
The accuracy and reliability of voice recognition are crucial to a positive user experience. Misinterpretations of commands can lead to frustration and incorrect waste disposal.
Accessibility Considerations
The design should cater to users with diverse needs and abilities. For visually impaired users, the system could incorporate audio cues and tactile feedback. For users with limited mobility, voice control and large, easily accessible buttons would be beneficial. Clear, concise instructions in multiple languages would also ensure accessibility for a broader user base. For example, the system could provide audio prompts in English, Spanish, and Mandarin.
Consideration for diverse needs ensures the system’s benefits are available to everyone.
Cost and Affordability
The price of smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling systems varies considerably, influenced by several key factors. Understanding this cost spectrum is crucial for homeowners weighing the investment against potential long-term benefits. This section will explore the price ranges, contributing factors, and a cost-benefit analysis to help you make an informed decision.Smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling systems represent a diverse market, with prices reflecting the sophistication of technology and included features.
Basic models, focusing primarily on automated disposal, can be found at a lower price point, while more advanced systems incorporating smart recycling features, app integration, and sophisticated sensors command a higher cost. Brand reputation also plays a significant role; established brands with a proven track record often charge a premium.
Price Ranges and Influencing Factors
The cost of smart kitchen waste disposal systems can range from a few hundred dollars for simpler, less automated models to several thousand dollars for high-end, fully integrated systems with advanced features. Factors contributing to this price variation include the size and capacity of the unit, the type of disposal mechanism (e.g., grinding, compacting), the materials used in construction, the level of smart technology integration (e.g., app connectivity, sensor technology), and the brand reputation.
For example, a basic food waste disposer might cost around $200-$500, while a fully integrated system with automated sorting and smart app control could easily exceed $2000-$3000. This price difference reflects not only the technology involved but also the added convenience and efficiency these systems provide.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Households
While the initial investment in a smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling system might seem substantial, a cost-benefit analysis reveals potential long-term savings and environmental advantages. The most significant cost savings are typically associated with reduced waste disposal fees. Many municipalities charge based on the volume of waste produced; efficient disposal and recycling systems can significantly reduce this cost over time.
Additionally, these systems can minimize the need for purchasing extra garbage bags, saving money in the long run. Furthermore, the environmental benefits, such as reduced landfill waste and improved recycling rates, contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle, although quantifying this benefit in monetary terms is more complex.Consider a household generating approximately 10 kg of waste per week. With a standard waste disposal service costing $20 per month, this household spends $240 annually on waste disposal.
By adopting a system that reduces waste volume by 50% through efficient disposal and recycling, this household could save approximately $120 per year. While the initial investment in a smart system might be $1000, the savings accumulate over time, potentially offsetting the initial cost within a few years. The environmental benefits, though difficult to precisely quantify, add further value to the long-term equation.
The long-term return on investment should also include the value of convenience and time savings associated with automated waste management.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling is poised for significant advancements, driven by converging trends in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and material science. We can expect to see systems that are not only more efficient and convenient but also more environmentally friendly and integrated into our wider smart homes.The next generation of smart waste management systems will leverage these technological leaps to offer functionalities beyond what’s currently available.
These improvements will focus on increasing automation, improving sorting accuracy, and enhancing user experience.
Advancements in AI and Sensor Technology
AI and sophisticated sensor technologies are key drivers of future improvements. AI algorithms will be crucial in analyzing waste composition in real-time, optimizing sorting processes, and predicting maintenance needs. Improved sensor technologies, such as advanced optical sensors and hyperspectral imaging, will allow for more accurate identification and sorting of different materials, even those that are difficult to distinguish visually, like various types of plastics.
For example, a system could utilize near-infrared spectroscopy to identify the type of plastic and automatically direct it to the appropriate recycling bin, minimizing human error and contamination. This level of precision will significantly increase recycling rates and reduce landfill waste.
Material Science Innovations in Waste Processing
Advances in material science will also play a critical role. New biodegradable and compostable materials will reduce the amount of non-recyclable waste. Research into efficient and cost-effective methods for breaking down complex polymers will open new avenues for recycling materials previously considered difficult or impossible to recycle. Imagine a system that automatically breaks down certain plastics into their base components for reuse, reducing the need for landfills and improving resource utilization.
This is already being explored in the development of chemical recycling processes.
Future Innovations in Smart Waste Disposal Systems
Future smart kitchen waste disposal systems might incorporate features like automated waste compaction, significantly reducing the frequency of bin emptying. Self-cleaning mechanisms, using UV light or other sterilization techniques, could eliminate the need for manual cleaning, improving hygiene and reducing unpleasant odors. Integration with smart home assistants could allow for voice-activated commands to control the system and receive real-time updates on waste levels and recycling progress.
A system might even suggest recipes based on the food waste detected, promoting less waste generation in the first place. For example, an app could suggest using leftover vegetables in a soup or stew, reducing food waste and promoting healthier eating habits. Furthermore, advanced predictive maintenance algorithms will allow for proactive service scheduling, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal system performance.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
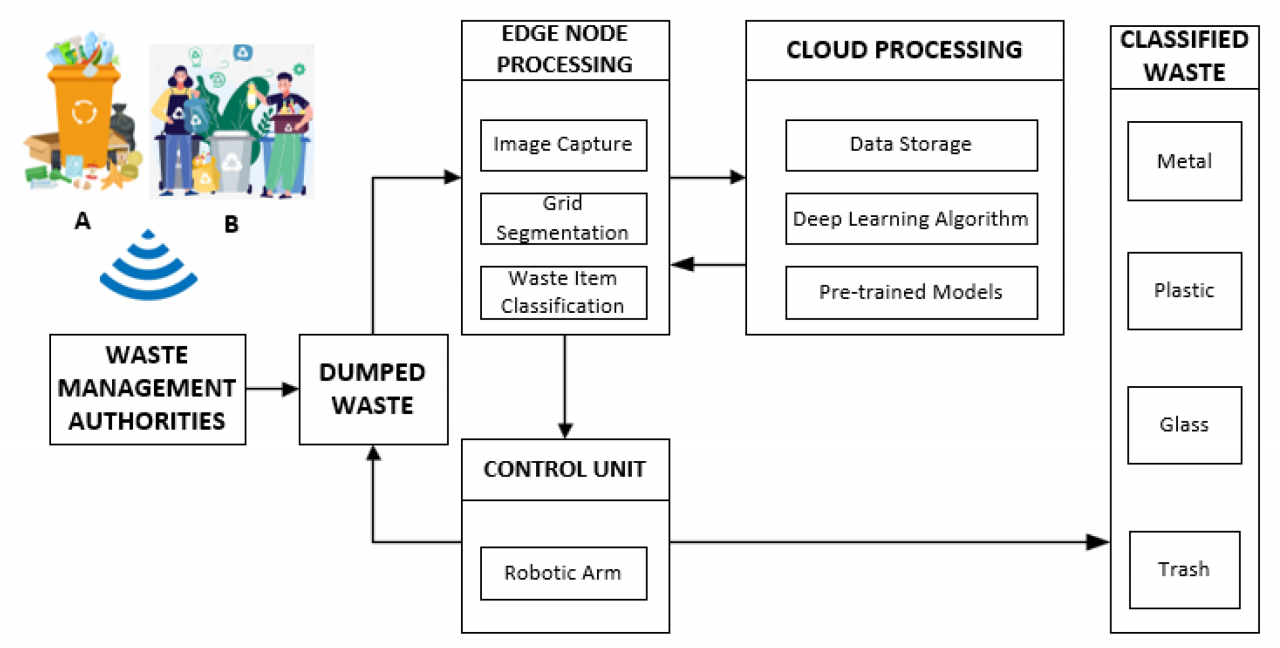
Source: mdpi.com
Keeping your smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling system running smoothly requires regular maintenance and understanding how to address common problems. Proper care will extend the lifespan of your system and prevent costly repairs. This section details common maintenance procedures and troubleshooting steps for various issues.
Common Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling system. These simple steps can significantly reduce the likelihood of malfunctions.
| Task | Frequency | Procedure | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emptying the waste and recycling containers | Daily or as needed | Remove the containers from the system and empty their contents into appropriate waste or recycling bins. Clean the containers with mild soap and water. | Prevents overflowing and odor build-up. Maintains hygiene. |
| Cleaning the system’s interior | Weekly | Use a damp cloth or sponge to wipe down the interior surfaces of the system, removing any food debris or spills. Avoid harsh chemicals. | Prevents bacterial growth and unpleasant odors. |
| Checking and cleaning sensors | Monthly | Gently wipe down any sensors with a soft, dry cloth. Avoid using liquids or abrasive cleaners. | Ensures accurate waste detection and prevents sensor malfunctions. |
| Inspecting for blockages | As needed | Check for any blockages in the waste or recycling chutes. Use a long, thin tool to carefully remove any obstructions. | Prevents system jams and ensures smooth operation. |
| Software updates | As prompted | Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to update the system’s software. This often includes bug fixes and performance improvements. | Improves functionality, adds new features, and enhances security. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing common problems promptly can prevent minor issues from escalating into major malfunctions. The table below Artikels solutions for several frequently encountered problems.
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| System not responding | Power outage, software glitch, sensor malfunction | Check power supply, try restarting the system, check for software updates, inspect sensors for obstructions. | Regular software updates, checking power supply regularly, avoiding overloading the system. |
| Inaccurate waste sorting | Obstructed or dirty sensors, incorrect waste disposal | Clean sensors, ensure correct waste disposal practices are followed, check for software updates. | Regular sensor cleaning, proper user training on waste sorting. |
| System jam | Overfilled containers, large or improperly disposed items | Empty containers, remove obstructions, check for items that shouldn’t be disposed of in the system. | Avoiding overloading the system, following guidelines on acceptable waste types. |
| Error messages | Various system issues | Consult the user manual for specific error codes and troubleshooting steps. Contact customer support if needed. | Regular maintenance, following user instructions. |
| Unpleasant odors | Food waste decomposition, unclean containers | Empty and clean containers thoroughly, ensure proper disposal of food waste. | Regular cleaning, prompt emptying of containers. |
Final Conclusion
Ultimately, smart kitchen waste disposal and recycling solutions offer a compelling blend of convenience and environmental responsibility. By embracing these technologies, we can significantly reduce landfill waste, conserve resources, and contribute to a more sustainable future. While the initial investment might seem significant, the long-term benefits – both environmental and in terms of time saved – make these systems a worthwhile consideration for eco-conscious homeowners.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and user-friendly solutions to emerge, making waste management a seamless and almost invisible part of our daily lives.
User Queries
What are the typical energy consumption levels of smart waste disposal systems?
Energy consumption varies greatly depending on the system’s features and size. Generally, it’s relatively low, comparable to other small kitchen appliances. Check the specific model’s specifications for details.
How do I clean and maintain a smart recycling bin?
Most smart bins have easily removable inner containers for simple cleaning. Refer to your specific model’s manual for cleaning instructions and recommended frequency.
What happens if the sensors in my smart recycling system malfunction?
Many systems have troubleshooting guides or customer support readily available. Often, a simple reboot or sensor cleaning can resolve the issue. More complex problems might require contacting the manufacturer.
Are smart waste disposal systems compatible with all types of waste?
Compatibility varies. Some systems handle a wider range of materials than others. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines for acceptable waste types to avoid damage or malfunction.
Can I install a smart waste disposal system myself, or do I need a professional?
Installation requirements vary depending on the system. Some are plug-and-play, while others might require professional installation, particularly for integrated systems. Consult the installation guide before attempting installation.












