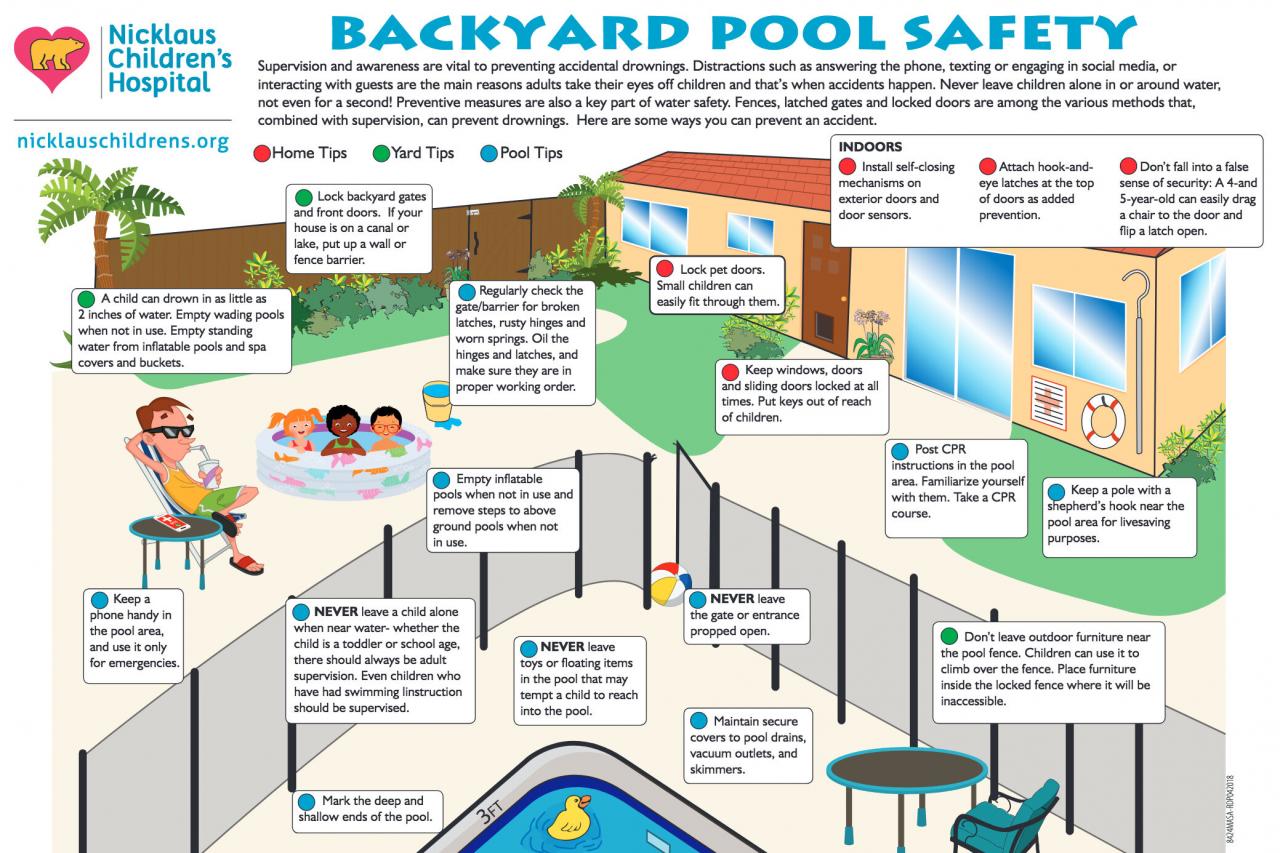
Outdoor pool safety features for children and adults are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring everyone enjoys a fun and safe swimming experience. From proper fencing and pool covers to vigilant supervision and readily available emergency equipment, numerous strategies contribute to a secure environment. This guide explores essential safety measures, covering everything from pool design and maintenance to water safety education and emergency response protocols.
Understanding these factors is vital for creating a welcoming and safe space for swimmers of all ages and abilities.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of pool safety, emphasizing proactive measures to prevent accidents and the importance of preparedness for unforeseen events. We’ll examine effective supervision techniques, the benefits of swimming lessons and CPR training, and the proper maintenance and chemical handling procedures necessary for a healthy and safe pool environment. We’ll also discuss the importance of accessibility for all, ensuring that everyone can enjoy the refreshing benefits of a swim.
Drowning Prevention Techniques
Drowning is a silent killer, often happening quickly and without warning. Understanding common drowning scenarios and implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial for ensuring pool safety for both children and adults. This section details various techniques to minimize the risk of drowning in outdoor pools.
Common Drowning Scenarios, Outdoor pool safety features for children and adults
Drowning incidents in outdoor pools vary depending on age and circumstances. Children, especially toddlers and preschoolers, are at high risk due to their limited swimming abilities and lack of awareness of water hazards. They may fall into the pool unattended or while playing near the edge. Adults may drown due to sudden medical emergencies, alcohol or drug impairment, or even a simple lapse in attention while swimming.
In many cases, drowning is silent and happens quickly, often without splashing or yelling for help. A common scenario involves a child quietly slipping into the water and becoming submerged without anyone noticing immediately. Another involves an adult experiencing a heart attack or stroke while swimming and being unable to get to safety.
Supervising Children Around Pools
Effective supervision is paramount. For toddlers and preschoolers, constant, close supervision within arm’s reach is essential. This means a designated adult should never take their eyes off the child while they are near the pool. For older children, who may have some swimming skills, supervision should still be vigilant, though the distance can be slightly greater, but always within sight and earshot.
The adult should be actively engaged and avoid distractions like cell phones. Consider using a buddy system for older children, ensuring they swim with a friend and look out for each other. Clearly defined rules and expectations about pool safety should be established and reinforced regularly.
Pool Barriers and Fences
Properly designed and maintained pool barriers are critical. Fences should completely surround the pool area, be at least four feet high, have self-closing and self-latching gates that are out of reach of children, and be made of a material that is difficult for children to climb. The gate latch should be placed high enough to prevent children from reaching it easily.
Regular inspections are necessary to ensure the fence is in good repair and that the gate is functioning correctly. Local building codes often specify requirements for pool fencing; compliance is vital. For example, the International Swimming Pool and Spa Code (ISPSC) provides detailed guidelines on pool barrier construction.
Pool Safety Covers
Pool safety covers offer an additional layer of protection. These covers, available in various materials like mesh or solid, are designed to prevent accidental falls into the pool. Mesh covers allow water to drain through, while solid covers create a complete barrier. However, it’s crucial to understand that no safety cover is foolproof. They should be properly installed and maintained according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Regular checks for damage or wear are essential, and any issues should be addressed promptly. While they significantly reduce the risk, constant supervision remains vital, especially with young children.
Pool Alarms
A comprehensive pool safety plan often includes alarms to provide additional warning of potential danger. Various types of alarms are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Alarm Type | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Alarm | Detects changes in water level; often placed in the pool. | Early warning of unauthorized entry. | Can be triggered by rain or other factors; may require regular maintenance. |
| Door/Gate Alarm | Sounds when a pool gate or access point is opened. | Reminds adults to supervise. | Relies on gate being properly closed and latched. |
| Motion-Sensing Alarm | Detects movement near the pool area. | Broader coverage; alerts to any presence near the pool. | Can be triggered by animals or other non-threatening movements; requires careful placement. |
| Combination Alarms | Integrates multiple alarm types. | Comprehensive protection; multi-layered safety. | Higher initial cost; may require more complex setup. |
Water Safety Education and Training
Water safety education and training are crucial for preventing drowning incidents, particularly among children. A comprehensive approach encompassing rules, swimming lessons, and emergency response training significantly reduces risks and promotes safer aquatic environments for everyone. This section details essential elements of a robust water safety program.
Essential Water Safety Rules for Children and Adults
Implementing clear and consistent water safety rules is paramount. Children should be taught never to swim alone, always to swim with a buddy, and to understand their limitations in the water. Adults should actively supervise children at all times near water, even if lifeguards are present. Knowing how to perform a safe entry and exit from the pool is also essential, along with understanding the importance of staying within designated swimming areas and avoiding running or horseplay near the water.
Adults should model responsible behavior, demonstrating respect for water safety rules. These rules apply regardless of swimming ability.
The Importance of Swimming Lessons and Their Impact on Drowning Incidents
Formal swimming lessons significantly reduce the risk of drowning. Studies consistently show that children who have received swimming instruction are less likely to experience a drowning incident. Swimming lessons teach essential water survival skills, such as floating, treading water, and basic swimming techniques. These skills provide children with the confidence and ability to cope with unexpected situations in the water.
Early enrollment in swimming lessons, ideally starting around age four, is particularly beneficial. The impact is substantial; properly trained swimmers have a significantly lower risk of drowning compared to those without formal training.
Benefits of CPR and First Aid Training for Poolside Safety
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) and first aid training are vital skills for anyone who spends time around a pool. Knowing how to perform CPR can be life-saving in the event of a drowning or near-drowning incident. Immediate CPR can significantly increase the chances of survival. First aid training equips individuals to handle other pool-related injuries, such as cuts, scrapes, and heat exhaustion.
Even basic first aid knowledge can make a significant difference in managing injuries until professional medical help arrives. Regular refresher courses are recommended to maintain proficiency in these life-saving skills.
Emergency Procedures for Pool Accidents: An Infographic
The following infographic details emergency procedures for pool accidents.
| Section | Visual Description | Text Description |
|---|---|---|
| Accident Recognition | A simple illustration of a person submerged in water, another struggling at the surface, and a third person appearing unresponsive on the pool deck. | Immediately recognize signs of distress: submerged person, struggling swimmer, or unresponsive individual near the water. |
| Call for Help | An image of a person calling emergency services on a mobile phone, while another is running to get help. | Call emergency services (911 or your local equivalent) immediately. If possible, send someone else to get help. |
| Rescue (If Trained) | An image depicting a trained rescuer reaching a struggling person with a rescue aid (e.g., reaching pole or flotation device). | If trained and it’s safe to do so, attempt a rescue using appropriate techniques and equipment. Prioritize your safety. |
| CPR and First Aid | An image showing chest compressions and rescue breaths being administered. | Begin CPR and administer first aid as needed until emergency services arrive. |
| Post-Incident Care | An image depicting medical personnel attending to the victim. | Cooperate with emergency medical personnel. |
Resources for Water Safety Education and Training Programs
Access to water safety education and training is crucial. Numerous organizations offer courses and resources to the public.
- Local YMCA or Community Centers: Many offer swimming lessons and water safety courses for all ages.
- American Red Cross: Provides comprehensive water safety training, including lifeguarding, CPR, and first aid certifications.
- United States Swim School Association (USSSA): Offers resources and information on finding reputable swim schools.
- Local Parks and Recreation Departments: Often offer swimming lessons and water safety programs.
- Private Swim Schools: Numerous private schools provide tailored swimming instruction and safety programs.
Pool Maintenance and Chemical Safety
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
Maintaining a clean and properly balanced pool is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring everyone’s safety and enjoyment. Neglecting pool maintenance can lead to serious health risks and create hazardous conditions, particularly for children. This section details the essential aspects of pool maintenance and safe chemical handling.
Potential Hazards of Improper Pool Maintenance
Improper pool maintenance creates several hazards. Unbalanced water chemistry can cause skin and eye irritation, respiratory problems, and damage to pool equipment. A lack of regular cleaning leads to the buildup of algae, bacteria, and other contaminants, increasing the risk of illness and creating slippery surfaces that contribute to falls and injuries. Furthermore, malfunctioning equipment, like faulty pumps or filters, can pose electrical hazards and create unsafe conditions.
For example, a cracked pool liner could lead to unexpected leaks and structural damage, making the pool unsafe.
Importance of Regular Pool Cleaning and Chemical Balancing
Regular pool cleaning and chemical balancing are paramount for maintaining a healthy and safe swimming environment. Cleaning removes debris, algae, and other contaminants, preventing the growth of harmful bacteria. Chemical balancing ensures the water is properly sanitized and prevents corrosion of pool equipment. Maintaining the proper pH level and sanitizer concentration minimizes health risks and extends the lifespan of the pool’s components.
For instance, consistently low pH levels can corrode the pool’s metal parts, while high pH levels can cause scaling and cloudiness, making the water uncomfortable to swim in.
Safe Handling and Storage of Pool Chemicals
Pool chemicals, such as chlorine and algaecides, are potent substances that require careful handling and storage. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a respirator, when handling these chemicals. Store chemicals in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from children and pets, in their original containers. Never mix different chemicals together, as this can create dangerous reactions.
For example, mixing chlorine and ammonia can produce toxic chloramine gas. Proper labeling and secure storage prevent accidental exposure and chemical reactions.
Proper Testing and Adjustment of Pool Water Chemistry
Regular testing of pool water chemistry is essential to maintain a safe and enjoyable swimming experience. Use a reliable test kit to measure pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels. Adjust chemical levels as needed, following the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Always add chemicals slowly and carefully, ensuring they are fully dissolved before allowing swimmers back into the pool. For example, adding too much chlorine at once can create “chlorine shock,” which can irritate swimmers’ eyes and skin.
Accurate testing and gradual adjustments are crucial for safe water conditions.
Routine Pool Maintenance Checklist
| Task | Frequency | Procedure | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skim pool surface | Daily | Remove leaves, insects, and other debris using a pool skimmer. | Remove debris promptly to prevent staining and bacterial growth. |
| Vacuum pool floor and walls | Weekly | Use a pool vacuum to remove dirt and debris from the bottom and sides of the pool. | Pay special attention to areas where debris tends to accumulate. |
| Backwash filter | As needed (when pressure gauge indicates) | Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for backwashing the filter. | Backwashing removes trapped debris and improves filter efficiency. |
| Test and adjust water chemistry | Weekly | Test pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels. Adjust as needed using appropriate chemicals. | Maintain optimal levels for safe and clear water. |
| Clean pool baskets | Weekly | Empty and clean the pump and skimmer baskets to remove debris. | Regular cleaning prevents blockages and ensures proper filtration. |
| Check and clean pool equipment | Monthly | Inspect pumps, filters, and other equipment for damage or malfunctions. Clean as needed. | Early detection of problems prevents costly repairs. |
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Poolside emergencies require swift and coordinated action. Being prepared can significantly impact the outcome of an accident, potentially saving lives. This section Artikels crucial steps for handling pool-related emergencies, from prevention to post-incident care.
Steps to Take in Case of a Pool-Related Emergency
Immediate action is paramount in any pool emergency. A calm and organized response is key to minimizing harm. First, assess the situation quickly and safely, ensuring your own safety before attempting any rescue. Then, activate your emergency plan, which should include alerting emergency services and trained personnel.
Ensuring outdoor pool safety for kids and adults involves things like proper fencing and adult supervision. Keeping the pool clean is crucial for hygiene and safety, and luckily, you can learn how to do this yourself by checking out this guide on how to maintain a swimming pool without hiring a professional. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and chemical balancing, contributes significantly to a safer and more enjoyable swimming experience for everyone.
Basic First Aid and CPR in a Pool Setting
Administering first aid and CPR effectively in a pool environment presents unique challenges. The water itself can complicate rescue and resuscitation efforts. It’s crucial to have appropriate training in water rescue techniques and pool-specific CPR procedures, which account for removing water from the victim’s airway before initiating chest compressions. Properly trained lifeguards are essential for this purpose.
For those without formal training, the focus should be on activating emergency medical services (EMS) immediately.
Keeping an outdoor pool safe for kids and adults involves layers of protection, from fences and self-closing gates to adult supervision. However, a clean pool is also a safer pool, so regular maintenance is key. Check out these swimming pool cleaning tips for beginners with small budgets to keep your pool sparkling and minimize potential hazards.
Proper cleaning contributes significantly to a safer swimming environment for everyone.
Importance of Readily Available Emergency Contact Information
Having easily accessible emergency contact information is crucial. This should include numbers for local emergency services, poison control (if chemical incidents are involved), and pre-designated contacts for family members or responsible adults. This information should be prominently displayed near the pool area, ideally in a waterproof container. Consider creating a laminated card with all essential information.
Local Emergency Services and Response Times
Knowledge of your local emergency services and their approximate response times is vital. This information varies by location, so it’s crucial to research and confirm the contact details for your specific area. Familiarize yourself with the local fire department, ambulance service, and police department numbers. Consider noting the estimated response time based on your location’s distance from the nearest emergency services.
For example, if you live in a rural area, response times might be significantly longer than in a city.
Handling a Drowning Victim: A Step-by-Step Procedure
A drowning incident requires a systematic approach. Speed and efficiency are critical, as every second counts. The following steps Artikel a procedure for handling a drowning victim, from rescue to emergency medical care:
- Assess the scene: Ensure your own safety before approaching the victim. If the victim is unconscious and submerged, immediately call emergency services.
- Reach or throw: If possible, reach the victim with a pole or extendable object. If that’s not feasible, throw a flotation device like a life ring.
- Wading rescue: Only enter the water if you’re a trained rescuer and it’s safe. Approach the victim from behind to avoid struggling.
- Tow the victim to safety: Use a safe towing technique to bring the victim to shore. Avoid direct contact with the victim’s face to prevent further injury.
- Remove the victim from the water: Carefully remove the victim from the water, supporting their head and neck to prevent spinal injury.
- Check for responsiveness: Check if the victim is responsive by gently shaking their shoulders and asking if they are okay.
- Initiate CPR if necessary: If the victim is unresponsive and not breathing normally, immediately begin CPR. If trained, perform rescue breaths to clear the airway of water first.
- Continue CPR until help arrives: Continue CPR until emergency medical services arrive and take over.
- Provide information to emergency responders: Provide the emergency responders with a clear account of the incident, including the victim’s condition and the steps taken.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Outdoor Pool Safety Features For Children And Adults
Creating accessible and inclusive pool environments is crucial for ensuring everyone can enjoy the benefits of swimming and water activities. Designing for accessibility not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances the overall usability and safety of the pool for all users. This includes considering the needs of people with various physical limitations, sensory sensitivities, and cognitive differences.
Designing accessible pools requires careful consideration of various design elements to create a safe and welcoming space for all. This involves incorporating features that make it easier for people with disabilities to access and use the pool independently and safely. The goal is to provide equal opportunities for recreation and exercise, fostering a sense of belonging and inclusion for everyone.
Pool Access Features for People with Disabilities
Adaptive equipment and thoughtful design are essential for ensuring accessibility. Ramps with appropriate gradients and handrails provide a gentle slope for wheelchair users and individuals with mobility impairments. Pool lifts, either permanently installed or portable, offer a safe and convenient way to enter and exit the water. These lifts typically consist of a sling seat that lowers the user into the water and raises them back out.
Transfer benches near the pool’s edge provide a stable surface for individuals who need assistance transferring from a wheelchair to a pool chair or into the water. Other adaptive equipment includes specialized pool wheelchairs designed for water use, and grab bars strategically placed around the pool deck and within the pool itself to provide stability and support.
Importance of Inclusive Pool Environments
Providing a safe and inclusive environment for all pool users is paramount. An accessible pool promotes physical and mental well-being for people with disabilities, allowing them to participate in recreational activities and improve their health. It also fosters a sense of community and belonging, breaking down barriers and promoting social inclusion. Inclusive design sends a powerful message that everyone is valued and welcome, regardless of their abilities.
Furthermore, accessible facilities demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility and equal opportunities.
Challenges and Solutions in Achieving Accessibility
While designing accessible pools offers many benefits, challenges can arise. Cost can be a significant factor, as installing ramps, lifts, and other adaptive equipment requires additional investment. Space limitations may also present challenges, especially in smaller pool areas. Finding qualified professionals experienced in designing and installing accessible pool features is another potential hurdle. Solutions to these challenges include exploring grants and funding opportunities specifically designed for accessibility projects, optimizing space utilization through creative design solutions, and collaborating with specialized accessibility consultants to ensure the project meets all relevant standards and guidelines.
Comparison of Pool Designs for Accessibility
Different pool designs offer varying levels of accessibility. The following table compares some common designs:
| Pool Design | Accessibility Features | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional In-ground Pool | May require ramps, lifts, and transfer benches to be added. | Widely available, various shapes and sizes. | Can be challenging to retrofit for accessibility. |
| Zero-Entry Pool | Features a gradual slope allowing direct entry from the pool deck. | Excellent accessibility, requires minimal adaptive equipment. | Can occupy a larger footprint than traditional pools. |
| Elevated Pool with Lift | Requires a lift for access, but offers a visually appealing design. | Can be aesthetically pleasing, suitable for various locations. | The cost of installation and maintenance of the lift is higher. |
| Indoor Pool with Accessible Changing Rooms | Provides protection from weather and easier access to changing facilities. | Offers climate control, suitable for all-weather use. | Requires more significant initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. |
Conclusion
Creating a safe and enjoyable outdoor pool environment requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing preventative measures, responsible supervision, and thorough emergency preparedness. By understanding and implementing the safety features discussed—from robust barriers and alarms to comprehensive water safety education and prompt emergency response protocols—we significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Remember, proactive safety is the cornerstone of a fun and worry-free swimming experience for everyone.
Popular Questions
What are some common causes of pool accidents besides drowning?
Slipping and falling on wet surfaces, chemical burns from improperly handled pool chemicals, and injuries from diving into shallow water are all common pool-related accidents.
How often should pool water be tested?
Pool water should be tested at least once a week, and more frequently during periods of heavy use or extreme weather.
What should I do if someone is experiencing a near-drowning incident?
Immediately call emergency services, then remove the person from the water and begin CPR if necessary. Follow the steps Artikeld in your local emergency response protocols.
Are there specific age recommendations for unsupervised swimming?
Children should never swim unsupervised, regardless of age or swimming ability. Constant adult supervision is essential.
What are some ways to make a pool more accessible to people with disabilities?
Ramps, lifts, and adaptive equipment can improve accessibility. Consider pool designs with varying depths and features to accommodate diverse needs.










